Top 50 React Interview Questions You Must Prepare In 2020
Top 50 React Interview Questions You Must Prepare In 2020
General React – React Interview Questions
1. Differentiate between Real DOM and Virtual DOM.
| Real DOM | Virtual DOM |
|---|---|
| 1. It updates slow. | 1. It updates faster. |
| 2. Can directly update HTML. | 2. Can’t directly update HTML. |
| 3. Creates a new DOM if element updates. | 3. Updates the JSX if element updates. |
| 4. DOM manipulation is very expensive. | 4. DOM manipulation is very easy. |
| 5. Too much of memory wastage. | 5. No memory wastage. |
2. What is React?
- React is a front-end JavaScript library developed by Facebook in 2011.
- It follows the component based approach which helps in building reusable UI components.
- It is used for developing complex and interactive web and mobile UI.
- Even though it was open-sourced only in 2015, it has one of the largest communities supporting it.
3. What are the features of React?
Major features of React are listed below:
- It uses the virtual DOM instead of the real DOM.
- It uses server-side rendering.
- It follows uni-directional data flow or data binding.
4. List some of the major advantages of React.
Some of the major advantages of React are:
- It increases the application’s performance
- It can be conveniently used on the client as well as server side
- Because of JSX, code’s readability increases
- React is easy to integrate with other frameworks like Meteor, Angular, etc
- Using React, writing UI test cases become extremely easy
5. What are the limitations of React?
Limitations of React are listed below:
- React is just a library, not a full-blown framework
- Its library is very large and takes time to understand
- It can be little difficult for the novice programmers to understand
- Coding gets complex as it uses inline templating and JSX
6. What is JSX?
JSX is a shorthand for JavaScript XML. This is a type of file used by React which utilizes the expressiveness of JavaScript along with HTML like template syntax. This makes the HTML file really easy to understand. This file makes applications robust and boosts its performance. Below is an example of JSX:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| render(){ return( <div> <h1> Hello World from Edureka!!</h1> </div> );} |
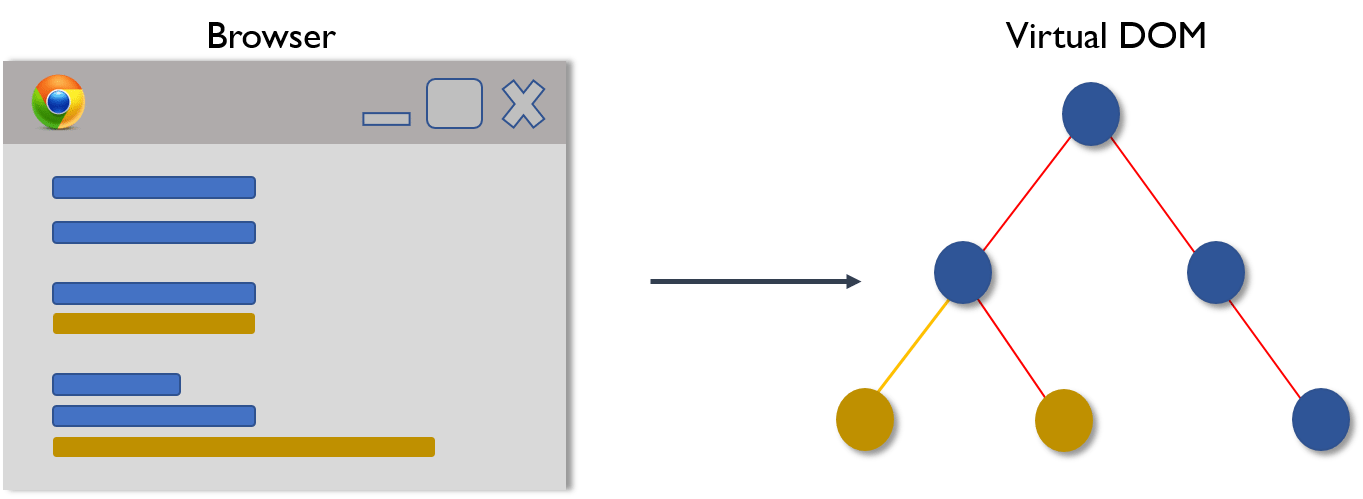
A virtual DOM is a lightweight JavaScript object which originally is just the copy of the real DOM. It is a node tree that lists the elements, their attributes and content as Objects and their properties. React’s render function creates a node tree out of the React components. It then updates this tree in response to the mutations in the data model which is caused by various actions done by the user or by the system.
This Virtual DOM works in three simple steps.
This Virtual DOM works in three simple steps.
- Whenever any underlying data changes, the entire UI is re-rendered in Virtual DOM representation.
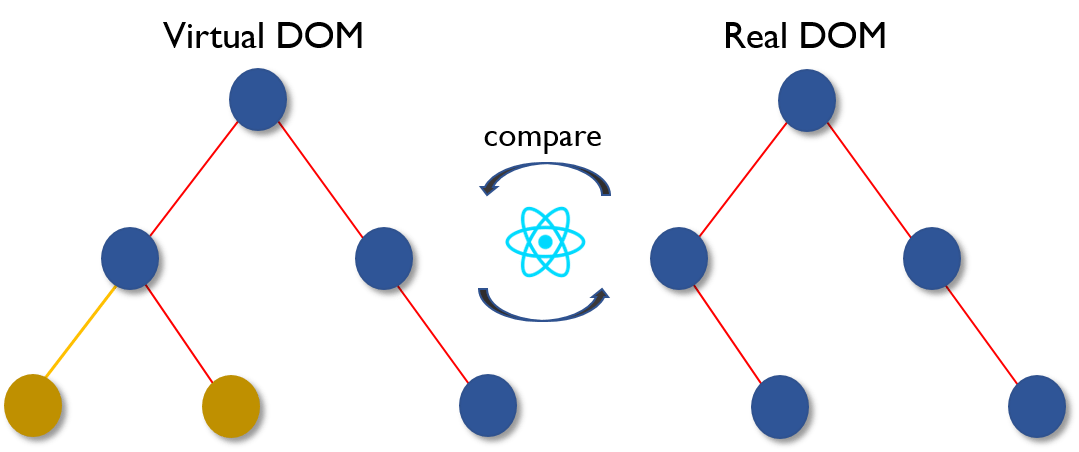
- Then the difference between the previous DOM representation and the new one is calculated.
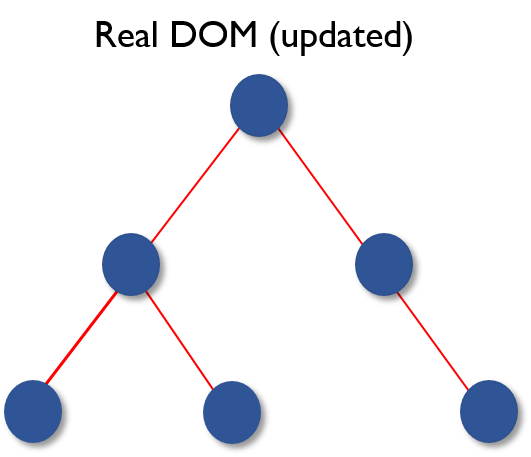
- Once the calculations are done, the real DOM will be updated with only the things that have actually changed.
8. Why can’t browsers read JSX?
Browsers can only read JavaScript objects but JSX in not a regular JavaScript object. Thus to enable a browser to read JSX, first, we need to transform JSX file into a JavaScript object using JSX transformers like Babel and then pass it to the browser.
9. How different is React’s ES6 syntax when compared to ES5?
Syntax has changed from ES5 to ES6 in following aspects:
- require vs import12345
// ES5var React = require('react');// ES6importReact from'react'; - export vs exports12345
// ES5module.exports = Component;// ES6exportdefaultComponent; - component and function12345678910111213141516171819
// ES5var MyComponent = React.createClass({render: function() {return<h3>Hello Edureka!</h3>;}});// ES6classMyComponentextendsReact.Component {render() {return<h3>Hello Edureka!</h3>;}} - props1234567891011121314151617181920
// ES5var App = React.createClass({propTypes: { name: React.PropTypes.string },render: function() {return<h3>Hello, {this.props.name}!</h3>;}});// ES6classAppextendsReact.Component {render() {return<h3>Hello, {this.props.name}!</h3>;}} - state1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526
// ES5var App = React.createClass({getInitialState: function() {return{ name:'world'};},render: function() {return<h3>Hello, {this.state.name}!</h3>;}});// ES6classAppextendsReact.Component {constructor() {super();this.state = { name:'world'};}render() {return<h3>Hello, {this.state.name}!</h3>;}}
10. How is React different from Angular?
| TOPIC | REACT | ANGULAR |
|---|---|---|
| 1. ARCHITECTURE | Only the View of MVC | Complete MVC |
| 2. RENDERING | Server-side rendering | Client-side rendering |
| 3. DOM | Uses virtual DOM | Uses real DOM |
| 4. DATA BINDING | One-way data binding | Two-way data binding |
| 5. DEBUGGING | Compile time debugging | Runtime debugging |
| 6. AUTHOR |
React Components – React Interview Questions
11. What do you understand from “In React, everything is a component.”
Components are the building blocks of a React application’s UI. These components split up the entire UI into small independent and reusable pieces. Then it renders each of these components independent of each other without affecting the rest of the UI.
12. Explain the purpose of render() in React.
Each React component must have a render() mandatorily. It returns a single React element which is the representation of the native DOM component. If more than one HTML element needs to be rendered, then they must be grouped together inside one enclosing tag such as <form>, <group>,<div> etc. This function must be kept pure i.e., it must return the same result each time it is invoked.
13. How can you embed two or more components into one?
We can embed components into one in the following way:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{ render(){ return( <div> <h1>Hello</h1> <Header/> </div> ); }}class Header extends React.Component{ render(){ return<h1>Header Component</h1> };}ReactDOM.render( <MyComponent/>, document.getElementById('content')); |
14. What is Props?
Props is the shorthand for Properties in React. They are read-only components which must be kept pure i.e. immutable. They are always passed down from the parent to the child components throughout the application. A child component can never send a prop back to the parent component. This help in maintaining the unidirectional data flow and are generally used to render the dynamically generated data.
15. What is a state in React and how is it used?
States are the heart of React components. States are the source of data and must be kept as simple as possible. Basically, states are the objects which determine components rendering and behavior. They are mutable unlike the props and create dynamic and interactive components. They are accessed via this.state().
16. Differentiate between states and props.
| Conditions | State | Props |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Receive initial value from parent component | Yes | Yes |
| 2. Parent component can change value | No | Yes |
| 3. Set default values inside component | Yes | Yes |
| 4. Changes inside component | Yes | No |
| 5. Set initial value for child components | Yes | Yes |
| 6. Changes inside child components | No | Yes |
17. How can you update the state of a component?
State of a component can be updated using this.setState().
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class MyComponent extends React.Component { constructor() { super(); this.state = { name: 'Maxx', id: '101' } } render() { setTimeout(()=>{this.setState({name:'Jaeha', id:'222'})},2000) return ( <div> <h1>Hello {this.state.name}</h1> <h2>Your Id is {this.state.id}</h2> </div> ); } }ReactDOM.render( <MyComponent/>, document.getElementById('content')); |
18. What is arrow function in React? How is it used?
Arrow functions are more of brief syntax for writing the function expression. They are also called ‘fat arrow‘ (=>) the functions. These functions allow to bind the context of the components properly since in ES6 auto binding is not available by default. Arrow functions are mostly useful while working with the higher order functions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| //General wayrender() { return( <MyInput onChange={this.handleChange.bind(this) } /> );}//With Arrow Functionrender() { return( <MyInput onChange={ (e) => this.handleOnChange(e) } /> );} |
19. Differentiate between stateful and stateless components.
| Stateful Component | Stateless Component |
|---|---|
| 1. Stores info about component’s state change in memory | 1. Calculates the internal state of the components |
| 2. Have authority to change state | 2. Do not have the authority to change state |
| 3. Contains the knowledge of past, current and possible future changes in state | 3. Contains no knowledge of past, current and possible future state changes |
| 4. Stateless components notify them about the requirement of the state change, then they send down the props to them. | 4. They receive the props from the Stateful components and treat them as callback functions. |
20. What are the different phases of React component’s lifecycle?
There are three different phases of React component’s lifecycle:
- Initial Rendering Phase: This is the phase when the component is about to start its life journey and make its way to the DOM.
- Updating Phase: Once the component gets added to the DOM, it can potentially update and re-render only when a prop or state change occurs. That happens only in this phase.
- Unmounting Phase: This is the final phase of a component’s life cycle in which the component is destroyed and removed from the DOM.
21. Explain the lifecycle methods of React components in detail.
Some of the most important lifecycle methods are:
- componentWillMount() – Executed just before rendering takes place both on the client as well as server-side.
- componentDidMount() – Executed on the client side only after the first render.
- componentWillReceiveProps() – Invoked as soon as the props are received from the parent class and before another render is called.
- shouldComponentUpdate() – Returns true or false value based on certain conditions. If you want your component to update, return true else return false. By default, it returns false.
- componentWillUpdate() – Called just before rendering takes place in the DOM.
- componentDidUpdate() – Called immediately after rendering takes place.
- componentWillUnmount() – Called after the component is unmounted from the DOM. It is used to clear up the memory spaces.
22. What is an event in React?
In React, events are the triggered reactions to specific actions like mouse hover, mouse click, key press, etc. Handling these events are similar to handling events in DOM elements. But there are some syntactical differences like:
- Events are named using camel case instead of just using the lowercase.
- Events are passed as functions instead of strings.
The event argument contains a set of properties, which are specific to an event. Each event type contains its own properties and behavior which can be accessed via its event handler only.
23. How do you create an event in React?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Display extends React.Component({ show(evt) { // code }, render() { // Render the div with an onClick prop (value is a function) return ( <div onClick={this.show}>Click Me!</div> ); }}); |
24. What are synthetic events in React?
Synthetic events are the objects which act as a cross-browser wrapper around the browser’s native event. They combine the behavior of different browsers into one API. This is done to make sure that the events show consistent properties across different browsers.
25. What do you understand by refs in React?
Refs is the short hand for References in React. It is an attribute which helps to store a reference to a particular React element or component, which will be returned by the components render configuration function. It is used to return references to a particular element or component returned by render(). They come in handy when we need DOM measurements or to add methods to the components.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class ReferenceDemo extends React.Component{ display() { const name = this.inputDemo.value; document.getElementById('disp').innerHTML = name; }render() { return( <div> Name: <input type="text" ref={input => this.inputDemo = input} /> <button name="Click" onClick={this.display}>Click</button> <h2>Hello <span id="disp"></span> !!!</h2> </div> ); } } |
I hope this set of React Interview Questions and Answers will help you in preparing for your interviews. All the best!
Comments
Post a Comment